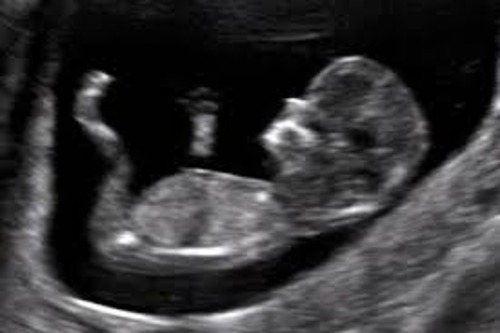
Introduction
The Nuchal Translucency (NT) scan is a specialized ultrasound performed early in pregnancy, typically between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation. This time frame is crucial as it allows for accurate measurement of the nuchal translucency and optimal assessment of the baby’s risk for chromosomal abnormalities. This screening test helps assess conditions such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13), which can lead to varying degrees of physical and intellectual disabilities.
Down syndrome occurs in about 1 in 700 births, while Edwards and Patau syndromes are rarer but often have more severe complications. The NT scan plays a key role in early detection, helping parents and healthcare providers make informed decisions about further testing and prenatal care. By identifying potential risks early, it enables timely interventions and support, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
What Is the Purpose of the NT Scan?
The NT scan provides key insights into the baby’s development, helping detect potential risks. It guides healthcare providers in tailoring prenatal care, determining the need for further tests, and preparing for interventions or specialized care during delivery.
✓ Visualizes Fetal Development : Uses ultrasound to monitor the baby’s growth, anatomy, and overall well-being.
✓ Measures Nuchal Translucency Thickness : Assesses the fluid-filled space at the back of the baby’s neck.
✓ Guides Risk Assessment : by combining ultrasound data, maternal age, and other factors to detect abnormalities.
How Is the NT Scan Performed?
Interpreting the Results
What Does the NT Scan Assess?
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Identifies risks for Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome.
Structural Issues
In some cases, a thickened NT may indicate congenital heart defects or other anomalies.
Accuracy and Limitations
Accuracy
✓ The NT scan is an effective screening tool but not diagnostic; it helps identify high-risk pregnancies.
✓ When combined with blood tests, NT screening improves accuracy in assessing chromosomal abnormality risks.
Limitations
✓ Results may be affected by factors like fetal position, maternal BMI, or the sonographer’s expertise.
✓ Only diagnostic tests like chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis can confirm abnormalities.
What Happens After the NT Scan?
Low Risk:
If results indicate a low risk, routine prenatal care continues without additional interventions.
High Risk:
If the scan shows a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities, healthcare providers may recommend further testing, such as:
✓ Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT): A blood test analyzing fetal DNA.
✓ Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): A diagnostic test that examines placental tissue.
✓ Amniocentesis: A test analyzing amniotic fluid to confirm or rule out chromosomal conditions.
Why Is the NT Scan Important?
The NT scan empowers expectant parents and healthcare providers with early insights into the baby’s development. For example, identifying a higher risk of Down syndrome early on allows parents to pursue diagnostic tests like CVS or amniocentesis, leading to informed decisions about medical care, specialized support, or preparations for postnatal treatment. This knowledge enables:
✓ Informed Decision-Making: Helps parents evaluate risks and decide if further diagnostic tests like CVS or amniocentesis are necessary.
✓ Early Interventions: Detects potential issues early, enabling timely medical care, specialist consultations, and birth planning.
✓ Reassurance: Offers peace of mind for low-risk pregnancies, reducing anxiety and providing confidence in fetal health.
✓ Conclusion: The NT scan is a vital part of early pregnancy care, offering valuable information about the baby’s risk for chromosomal abnormalities. While it is not a diagnostic test, it helps identify pregnancies that may benefit from further testing or monitoring. If you have concerns about your NT scan results, discuss them with your healthcare provider, who can guide you on the next steps for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
FAQ
A Nuchal Translucency (NT) scan is a specialized ultrasound performed during early pregnancy, typically between 11 and 14 weeks gestation. It assesses the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13).
The NT scan is usually performed between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy, as this is the optimal time to measure the nuchal translucency.
The NT scan helps assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities and other genetic conditions in the baby. It can provide early insights into potential health concerns and guide further diagnostic testing if needed.
If the NT scan indicates a higher risk of abnormalities, your healthcare provider may recommend further diagnostic tests, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, to confirm the findings.
Yes, the NT scan is a non-invasive and completely safe procedure for both the mother and baby. It uses ultrasound technology to measure nuchal translucency.


